3.3.6 3D Printing
3D printing is a process of making a three dimensional object from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is done using additive processes. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object. There are also multiple kinds of 3D printing.
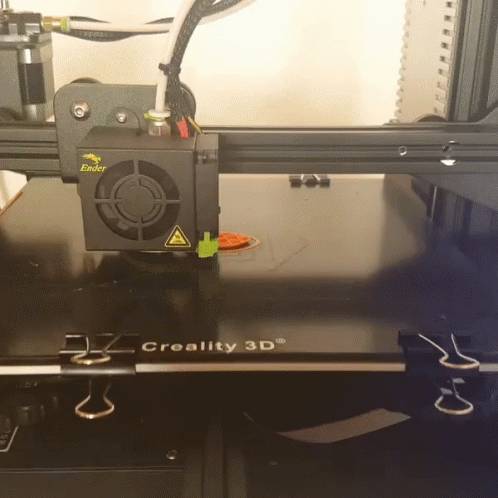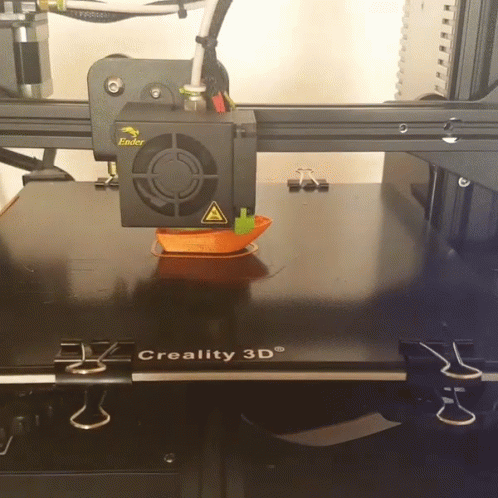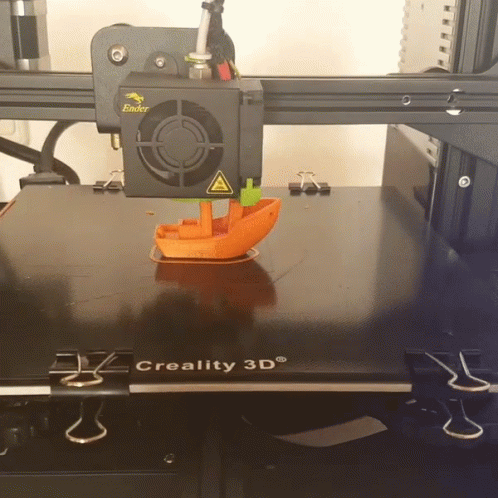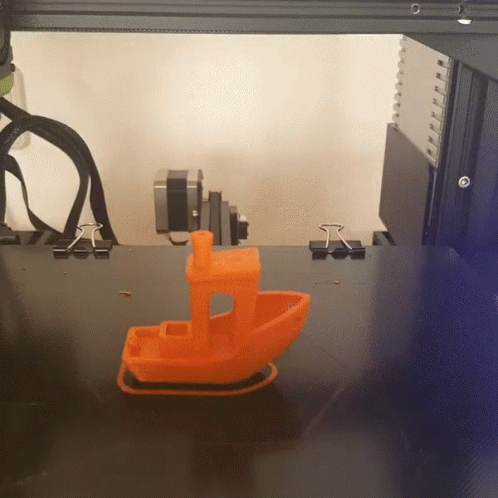 Above is an example of FDM 3D printing. This is the most common type of 3D printing. FDM stands for Fused Deposition Modeling. In this process, a filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle. The filament is then deposited in layers to build up the object. The nozzle moves in two directions, up and down, and in one direction, forward. The up and down movement is controlled by a motor and the forward movement is controlled by a computer. The computer tells the motor how far to move the nozzle up and down and how far to move the filament forward. The computer also tells the motor when to stop extruding filament. This process is repeated until the object is complete.
Above is an example of FDM 3D printing. This is the most common type of 3D printing. FDM stands for Fused Deposition Modeling. In this process, a filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle. The filament is then deposited in layers to build up the object. The nozzle moves in two directions, up and down, and in one direction, forward. The up and down movement is controlled by a motor and the forward movement is controlled by a computer. The computer tells the motor how far to move the nozzle up and down and how far to move the filament forward. The computer also tells the motor when to stop extruding filament. This process is repeated until the object is complete.
 Above is an example of SLA 3D printing. This is a type of 3D printing where a liquid photopolymer is cured with a laser to create the object. The object is created by a layer of liquid photopolymer being spread across the build platform. The build platform then moves down a small amount. A laser then traces the outline of the object to be created. This cures the photopolymer in that area. The build platform then moves after the layer and the process is repeated until the object is complete.
Above is an example of SLA 3D printing. This is a type of 3D printing where a liquid photopolymer is cured with a laser to create the object. The object is created by a layer of liquid photopolymer being spread across the build platform. The build platform then moves down a small amount. A laser then traces the outline of the object to be created. This cures the photopolymer in that area. The build platform then moves after the layer and the process is repeated until the object is complete.
 Above is an example of SLS 3D printing. This is a type of 3D printing where a laser sintering process is used to create the object. The object is created by a layer of powdered material being spread across the build platform. A laser then traces the outline of the object to be created. This melts the powdered material in that area and it fuses to any other activated material. It then cools and hardens. The laser can move left, right, forward, and backward. This can make metal pieces that are very strong. The process is also very fast.
Above is an example of SLS 3D printing. This is a type of 3D printing where a laser sintering process is used to create the object. The object is created by a layer of powdered material being spread across the build platform. A laser then traces the outline of the object to be created. This melts the powdered material in that area and it fuses to any other activated material. It then cools and hardens. The laser can move left, right, forward, and backward. This can make metal pieces that are very strong. The process is also very fast.
3D Printing Materials
There are many different types of materials that can be used in 3D printing. The most common materials are thermoplastics and metals. Thermoplastics are plastics that can be melted and reformed. Metals are materials that are strong and conduct electricity. There are also other materials that can be used in 3D printing like ceramics, glass, and concrete.
Below is a table of some common materials, their thermal properties, and their uses.
| Material | Thermal Properties | Traits |
|---|---|---|
| PLA | Low melting point, low strength, low heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, biodegradable, low cost |
| ABS | High melting point, high strength, low heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, low cost |
| Nylon | High melting point, high strength, high heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, higher cost, special nozzles |
| Polycarbonate | High melting point, high strength, high heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, higher cost, special nozzles |
| TPU | Low melting point, low strength, high heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, low cost, special nozzles |
| PETG | High melting point, high strength, flexible | Commonly used in 3D printing, higher cost, special nozzles |
| PVA | Low melting point, low strength, low heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, low cost, dissolves in water |
| HIPS | Low melting point, low strength, low heat resistance | Commonly used in 3D printing, low cost, dissolves in water |
3D Printing Software
There are many different types of software that can be used to create 3D models. The most common software is Autodesk Fusion 360. This software is free for students and teachers. It is also very easy to use. There are also other software like Blender, TinkerCAD, and SketchUp. These are all free and easy to use. There also also pieces of software called slicers. These are used to convert the 3D model into a file that can be used by the 3D printer. The most common slicer is Cura. There are also other slicers like Simplify3D, Slic3r, and PrusaSlicer. Below is a table with some links to the most common software and explaining their uses.
| Software | Link | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Autodesk Fusion 360 | https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360/overview | 3D modeling, 3D printing, CNC machining, CAM |
| Blender | https://www.blender.org/ | 3D modeling, animation |
| TinkerCAD | https://www.tinkercad.com/ | 3D modeling, 3D printing |
| SketchUp | https://www.sketchup.com/ | 3D modeling, 3D printing |
| Cura | https://ultimaker.com/software/ultimaker-cura | Slicer for 3D printing |
| Simplify3D | https://www.simplify3d.com/ | Slicer for 3D printing |
| Slic3r | https://slic3r.org/ | Slicer for 3D printing |
| PrusaSlicer | https://www.prusa3d.com/prusaslicer/ | Slicer for 3D printing |
| Chitubox | https://www.chitubox.com/ | Slicer for resin 3D printing |